Mountains
The dictionary says that a mountain is ‘higher
and steeper than a hill’.
It is a type of land (landform) that rises above the surrounding terrain.
Mountains usually have steep, sloping sides and sharp
or slightly rounded ridges and peaks.
How
are Mountains Formed?
Types or Mountain
Mountains We've Climbed
Find Your Favourite Mountain
Highest Mountains
Mountain Ranges
Mountain Weather
Plants and Animals
People

This is the World's highest mountain, Mount Everest.
Generally,
mountains are landforms that rise above 600 metres.
Mountains can be found on every continent and even beneath the sea.
Mountains are made in a number of different ways and there are several
different types of mountain.
Mountains are home
to about one-tenth of the world’s people, they cover
one-fifth of the earth’s land surface, and can be found in 75
percent of the
world’s countries.
More than half of the world’s fresh water comes frommountains
and all the
world's major rivers have their source in mountains.
How are mountains formed?
Mountains are created over long periods of time by tremendous forces
in the earth.
Mountains are formed by volcanism, erosion, and disturbances or upliftas
in the earth's crust.
The Earth's crust
is made up of 6 huge slabs called plates, which fit together like a
jigsaw puzzle.
When two slabs of the Earth's crust smash into each other the land can
be pushed
upwards, forming mountains. Many of the greatest mountain ranges of
the world have formed
because of enormous collisions between continents.
Dome
Mountains

Dome mountains are
the made when huge amount of melted rock pushes its way up
under the earth without getting folded or breaking. The result is a
rounded dome.
As the dome is raised above surrounding land it is eroded. This erosion
causes peaks
and valleys to form.
Fold Mountains

This is K2, the World's second highest mountain
Fold
mountains are formed when two of the Earth's tectonic plates collide
head on.
Their edges crumble just like a piece of paper folds when it is pushed
together.
Examples of fold mountains include Himalayas in Asia, the Alps in Europe
and
the Andes in South America
Fault-block Mountains

Mount Whitney in the Sierra Nevada
These
mountains form when faults or cracks in the earth's crust force some
materials
or blocks of rock up and others down.
Instead of the earth
folding over, the earth fractures and the blocks are stacked on top
of each other.
Examples of fault-block mountains include the Sierra Nevada mountains
in North America and the Harz Mountains in Germany.
Volcanic Mountains

Mount Kilimanjaro, the Highest mountain in Africa
Volcanic Mountains are formed when molten rock, or magma, deep within
the earth,
erupts, and piles up on the surface.
Examples of Volcanic Mountains include Mount St. Helens in North America
and Mount Pinatubo in the Philippines.
Plateau Mountains (Erosion Mountains)

Slide Mountain
These are mountains that are really plateaus that have
worn down from erosion
over millions of years.
These mountains are really large areas of very high flat land.
Back to the Top
When we are in Years 5 and 6 we have the chance to
climb mountains !
Snowdon |
Yes
Tor |
| Elevation (meters): 1085 Range: Snowdonia Country: United Kingdom Continent: Europe Difficulty: Walk up Best months for climbing: May, June, July, August, September Nearest Town: Llanberis |
 |
 |
Elevation (meters): 610 Range: Dartmoor Country: United Kingdom Continent: Europe Difficulty: Walk up Best months for climbing: February, March, May, June, July, December Nearest Town: Okehampton |
| Snowdon is the highest mountain in Wales, located within the
Snowdonia region. |
Yes Tor is one of the five tors on Dartmoor
over 600m.
Dartmoor is a former mountain range from many millions of years ago when it was as high as Mount Everest. It has eroded away to about one 12th of their size leaving the granite tors behind. Yes Tor is the second highest there and can be sen from many miles away making it far more distinctive compared to its peers. Yes Tor is easy enogh in all conditions if you know what you are doing. Take care not to underestimate the moors as it is deep in dartmoor meaning that phone signals will not work and there are no roads so people can ill afford serious injury. Dartmoors mountains offer very good scrambling and some good rock climbing too so be sure to check out the rocky neighbors. |
If you want to find out about mountains in other parts of the world click here:
These are the highest mountains on each of the Earth's continents:
Mountain |
Continent |
Height |
Asia |
8,850
m |
|
South
America |
6,959
m |
|
North
America |
6,194
m |
|
Africa |
5,895
m |
|
Europe |
5,642
m |
|
Antarctica |
4,897
m |
|
Australasia |
4,884
m |
What
are the Highest, Tallest, and Largest Mountains on Earth ?
Back to the Top
A
mountain range is a group or chain of mountains that are close together.
Mountain ranges are usually separated from other mountain ranges by
mountain
passes and rivers.
The
Andes Mountains, which stretch more than 4,500 miles (7,200 km) through
seven
South American countries, form the longest mountain range in the world.
The Himalayas
The Himalayas are
the highest mountain range in the world. The world's highest mountain,
Mount Everest, is a part of the Himalayas.
The word Himalayas
means "Land of Snow." It is the greatest mountain range in
Asia and the home
to the highest (tallest) mountain peaks in the world. The range is 1500
miles long and runs
through Northeastern Pakistan, Northern India, Southern Tibet, Nepal,
Sikkim and Bhutan.
There are more than 30 peaks of the Himalayas which rise to heights
of 7,620 m (25,000 ft) or more.
The Himalayas is
one of the youngest mountain ranges in the world and it is still growing
higher.
Mount Everest is growing by about 4mm a year which doesn't sound much
but over ten thousand years thats 40 metres.
( The Earth is billions of years old so ten thousand years isn't really
that long. )
They are growing because two of the Earth's plates are pushing together.
The Indian Plate is moving north and pushing the Eurasion Plate upwards.
Click on this image to see this happening:
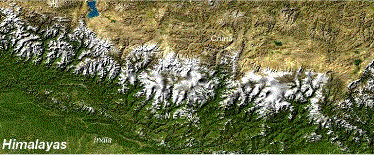
The
Himalayas seen from space.
The Alps
The Alps is a much
smaller mountain range than the Himalayas but its the biggest inEurope,
extending
over 750 miles (1,200 km) through South France, North Italy, Switzerland,
Liechtenstein, Germany, Austria and Slovenia.
The Alps includes
several hundred peaks and glaciers, including numerous peaks over
12,000 feet, with Mont Blanc highest at 15,771 feet.

Mont
Blanc is the higest peak in The Alps.
The Andes
The Andes Mountain
Range is the longest and one of the highest mountain ranges in the world.
They are located in South America and stretch 4,500 miles (7,200 km)
from north to south, along the west coast of the
continent.The Andes chain is generally about 200 miles (300 km) wide,
except in Bolivia, where it is 400 miles wide.
The Andes are the second highest Mountain Range in the world with many
peaks rising over 20,000 feet.
Mountain
Ranges on Each Continent
Antarctica: Antarctic Peninsula, Transantarctic Mountains
Africa: Atlas, Eastern African Highlands, Ethiopian Highlands
Asia: Hindu Kush, Himalayas, Taurus, Elburz, Japanese Mountains
Australasia: MacDonnell Mountains
Europe:
Pyrenees, Alps, Carpathians, Apennines, Urals, Balkan Mountains
North
America: Appalachians, Sierra Nevada, Rocky Mountains, Laurentides
South America: Andes, Brazilian Highlands
The
main differences in climate of mountains are temperature and moisture.
Mountains usually have much
wetter climates than the flat land around them. They get more rainfall
than low lying areas because the temperature
on the mountains is lower than the temperature at sea level. That is
why you often see snow on the top of
mountains all year round. The higher the place is above sea level the
colder it will be.
Climates change
rapidly on mountains, becoming colder the higher the altitude gets.
This happens because as you
get colder, air becomes thinner and is less able to absorb and hold
heat.
The cooler the temperature the less evaporation there is meaning that
there is more moisture in the air.
Some mountains reach higher than the clouds. At this altitude the extreme
cold and high winds cause blizzards.
Because
of the rapid changes in altitude and temperature on a mountain
slope, many different ecological can be The weather
can change very quickly on mountains. In just a few minutes
a thunder storm can roll in |
 |
If you climb from
the base to the peak of a big mountain, you will pass through a number
of different types of plants.
These plants provide the habitat for the different animals which can
be found at different heights.
This is what happens as you get higher and higher up a mountain:
The vegetation on the lower slopes depends on which climate
zone the mountain is in.
The foothills may be covered in broadleaved forests.
On the upper slopes coniferous trees like spruce
and pines.
As you climb higher it gets colder and colder and the trees eventually
thin out and disappear.
The highest parts of the mountain support only
sparse grasses and low-growing Alpine flowers
which can withstand the harsh conditions.
If the mountain is high enough all vegetation will disappear and the
peak is bare and rocky and
perhaps covered in snow and ice.
Climbers
and tourists visit them for the scenery. Farmers graze their animals
on them. Water authorities make reservoirs and pump the water to towns and cities. Forestry companies grow coniferous forests and harvest wood on them. There are also a lot of people living on them. |
 |
10% of the world's
6 billion people live on Mountains. That's 600 million people who rely
on mountains
for their survival and welfare.
These people have adapted to living in the mountains just like plants
and animals do.
A good example of this is the South American Uru tribe who have evolved
bigger hearts and lungs so they can breather the thin air at high altitudes.
Mountains can alos have a big affect on the people who live near them.
They make travel difficult.because Mountains can be very hard to cross.
They are often rugged and filled with forests and wild animals. The
weather can
be very poor and
unpredictableand the mountains may have no
natural 'passes,' or easy places to cross so that is travel dangerous.
All this means that
crossing over mountains - to trade goods or to fight a war - can be
a hard thingto do.
The people who live on mountains can often become isolated from the
rest of the world.
 |
Tourism |
 |
Mountains can aid
tourism and bring in money for the people who live there.
More than 50 million people visit mountains each year. Many mountain
towns around the world depend on tourists to support them.
People in the town provide food and lodging for tourists who come to
enjoy the nearby mountains.
Mountains can be
places for leisure activities. Many people like to ski on mountains.
Other people like
to climb mountains. Some people like to just visit mountains to take
photos and admire their beauty.
Other activities include mountaineering, paragliding, walking,
hiking, bird
watching, rafting,
mountain biking, skiing,
snow boarding, sledging, ice climbing and winter walking.
Tourism
is good because ..... |
Tourism
is bad because ..... |
|
it
brings in a lot of money. |
the environment can be permanently damaged. the price of land and food gets higher. of pollution from traffic. the mountains get eroded. litter gets dropped. local people can lose their cultural identity. |
